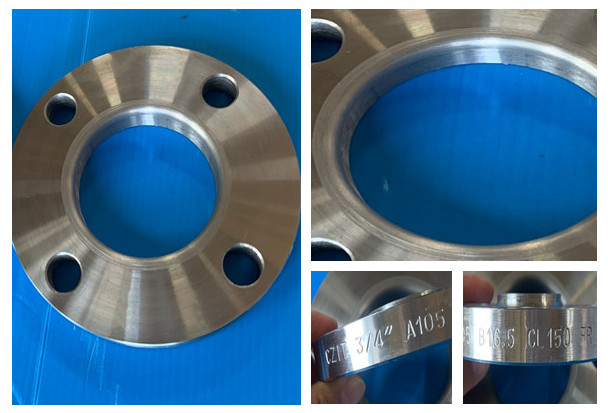
SPECIFICATION
| Product Name | Lap joint/Loose flange |
| Size | 1/2"-24" |
| Pressure | 150#-2500#,PN0.6-PN400,5K-40K |
| Standard | ANSI B16.5,EN1092-1, JIS B2220 etc. |
| Stub end | MSS SP 43, ASME B16.9 |
| Material | Stainless steel: A182F304/304L, A182 F316/316L, A182F321, A182F310S, A182F347H, A182F316Ti, 317/317L, 904L, 1.4301, 1.4307, 1.4401, 1.4571,1.4541, 254Mo and etc. |
| Carbon steel: A105, A350LF2, S235Jr, S275Jr, St37, St45.8, A42CP, A48CP, E24 , A515 Gr60, A515 Gr 70 etc. | |
| Duplex stainless steel: UNS31803, SAF2205, UNS32205, UNS31500, UNS32750 , UNS32760, 1.4462,1.4410,1.4501 and etc. | |
| Pipeline steel: A694 F42, A694F52, A694 F60, A694 F65, A694 F70, A694 F80 etc. | |
| Nickel alloy: inconel600, inconel625, inconel690, incoloy800, incoloy 825, incoloy 800H,C22, C-276, Monel400, Alloy20 etc. | |
| Cr-Mo alloy: A182F11, A182F5, A182F22, A182F91, A182F9, 16mo3,15Crmo, etc. | |
| Application | Petrochemical industry;aviation and aerospace industry;pharmaceutical industry;gas exhaust;power plant;ship building;water treatment,etc. |
| Advantages | ready stock,faster delivery time;available in all sizes,customized;high quality |
DIMENSION STANDARDS
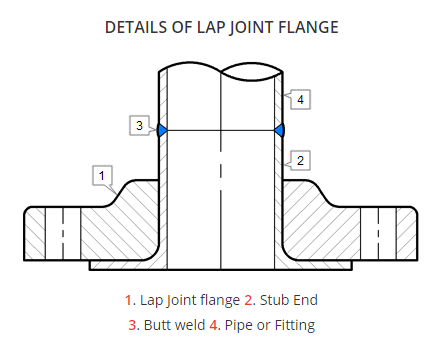
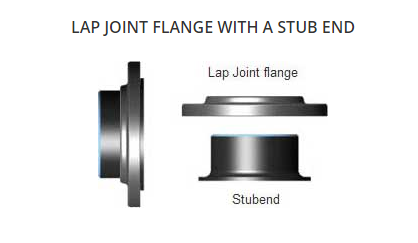
LAP JOINT FLANGE
A lap-joint flange requires two piping components for each side of the flanged connection, a stub end and a loose backing flange. The loose backing flange fits over the outside diameter of the stub end, which is butt-welded to the pipe. The backing flange is not welded to the pipe, and it can be rotated, which is particularly useful when it is necessary to orientate flanges during erection.
Also, as the backing flange does not come in contact with the process fluid, it can made of a less corrosive-resistant material. For example, if the process is corrosive and requires the pipe to be of stainless steel, as in ASTM A312 TP316L, then the stub end must also be made of SS 316L; however, the backing flange can be made of the cheaper ASTM A105.
This method of jointing is not as robust as a weld neck flange but is superior to screwed, socket weld, and slip on connections; however, it is more expensive to execute, because it require a full-penetration butt weld and requires two components.
STUB END
A Stub End always will be used with a Lap Joint flange, as a backing flange.
This flange connections are applied, in low-pressure and non critical applications, and is a cheap method of flanging.
In a stainless steel pipe system, for example, a carbon steel flange can be applied, because they are not come in contact with the product in the pipe.
Stub Ends are available in almost all pipe diameters. Dimensions and dimensional tolerances are defined in the ASME B.16.9 standard. Light-weight corrosion resistant Stub Ends (fittings) are defined in MSS SP43.
ADVANTAGED OF LAP JOINT FLANGE
- Freedom to swivel around the pipe facilitates the lining up of opposing flange bolt holes.
- Lack of contact with the fluid in the pipe often permits the use of inexpensive carbon steel flanges with corrosion resistant pipe.
- In systems which erode or corrode quickly, the flanges may be salvaged for re-use.
PRODUCTS DETAIL SHOW
1. Face
flat face, Radius is the most important
2. With hub or without hub
3.Face finish
The finish on the face of flange is measured as an Arithmetical Average Roughness Height(AARH). The finish is determined by the standard used. For example, ANSI B16.5 specifies face finishes within a range 125AARH-500AARH(3.2Ra to 12.5Ra). Other finishes are available on requst, for example 1.6 Ra max,1.6/3.2 Ra, 3.2/6.3Ra or 6.3/12.5Ra. The range 3.2/6.3Ra is most common.
MARKING AND PACKING
• Each layer use plastic film to protect the surface
• For all stainless steel are packed by plywood case. For bigger size carbon flange are packed by plywood pallet. Or can be customized packing.
• Shipping mark can make on request
• Markings on products can be carved or printed. OEM is accepted.
INSPECTION
• UT test
• PT test
• MT test
• Dimension test
Before delivery, our QC team will arrange NDT test and dimension inspection.Also accept TPI(third party inspection).
PRODUCTION PROCESS
| 1. Choose Genuine raw material | 2. Cut raw material | 3. Pre-heating |
| 4. Forging | 5. Heat treatment | 6. Rough Machining |
| 7. Drilling | 8. Fine maching | 9. Marking |
| 10. Inspection | 11. Packing | 12. Delivery |
-

ASME B16.48 CL150 CL300 Paddle spacer plank fla...
-

Screw BSP DIN PN 10/16 carbon steel A105 flange...
-

stainless steel forged lap joint loose flange c...
-

ASME b16.48 Factory Sale carbon steel figure 8 ...
-

WN ANSI B16.36 orifice weld neck flange with ja...
-

Socket weld flange A105 carbon steel SW RTJ 3/4...